Abstract
Introduction
The BMT-CTN 1204 study for Hemophagocytic Syndromes or Selected Primary Immune Deficiencies (NCT01998633) (RICHI) was a single arm study testing safety and efficacy of reduced intensity conditioning (RIC) with alemtuzumab (1mg/kg), fludarabine (150 mg/m2) and melphalan (140 mg/m2). Survival was favorable compared to historical studies, but patients experienced high rates of mixed chimerism (MC) and ultimate secondary graft failure (GF). Mechanisms for GF are not known. Expansion of recipient T cells and interferon-gamma pathway activation have been proposed as drivers for GF. However, high peri-transplant alemtuzumab levels have been associated with higher risk of MC and eventual secondary GF, suggesting an inverse relationship between GF and immune activation in the context of RIC. In order to elucidate mechanisms of GF for patients on the RICHI study, we systematically evaluated cytokine patterns and alemtuzumab levels and their association with durable engraftment.
Methods
Serial blood samples were collected, processed, and stored for consenting patients at day -14 (window: day -28 to -14), day -7 (+/- 1 day), day -1 (+/- 1), day +1 (+1 to +3), day +14 (+/- 2), day +28 (+/- 2), day +42 (+/- 3), day +70 (+/- 10), and day +100 (+/- 10). Alemtuzumab levels were measured using a flow cytometric assay as previously described. Comprehensive cytokine analysis was performed for over 100 analytes using the MagPix platform. Primary GF was defined as donor chimerism <5% prior to day +42. Secondary GF was defined as donor chimerism <5% after initial engraftment and/or requirement of donor lymphocyte infusion (DLI) or second HCT (with or without conditioning) to manage MC or graft loss. Mixed chimerism (MC) was defined as donor chimerism <95% on at least one occasion.
Results
Thirty-three patients were included in this study with HLH (n=25), CAEBV (n=3), CGD (n=2), HIGM (n=2), and IPEX (n=1). All patients received bone marrow grafts and 27 (82%) patients had unrelated donors. Twenty-one grafts were 8/8 or 6/6 HLA-matched (64%) and 12 grafts were 7/8 HLA-matched (36%). Among all patients, 1 patient (3%) developed primary GF, 22 (67%) developed mixed chimerism (MC), and 11 patients (33%) developed secondary GF. Survival with sustained engraftment without DLI or second HCT was 40.0%.
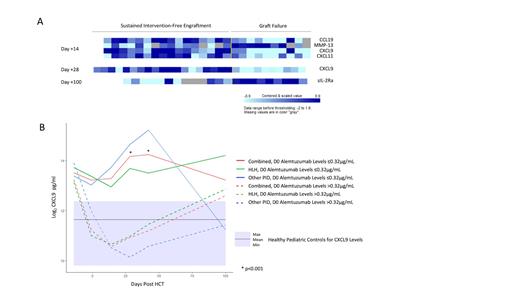
We first evaluated peripheral blood levels of 100+ cytokines. Analysis revealed significant differences between patients with and without GF as shown in Figure 1A. Notably, on day +14 and +28, patients with secondary GF had significantly lower CXCL9 levels than those without GF.
We then estimated the cumulative incidence (CI) of secondary GF among patients with CXCL9 levels above and below the day +14 median level of 2394pg/mL. The CI of secondary GF in patients with a day +14 CXCL9 level ≤2394pg/mL was 73.6% vs 0% in patients with a level >2394pg/mL (p=0.002). The CI of secondary GF in patients with a day +28 CXCL9 level ≤2867pg/mL (day +28 median) was 64.3%, vs 0% in patients with levels >2867pg/mL (p=0.004).
We then sought to correlate CXCL9 levels with alemtuzumab exposure, as high alemtuzumab levels would result in more efficient T cell depletion of donor grafts that could lead to lower CXCL9 levels. Indeed, CXCL9 levels inversely correlated with day 0 alemtuzumab levels. Patients with day 0 alemtuzumab levels >0.32µg/mL had lower CXCL9 levels compared to patients with levels ≤0.32µg/mL (Figure 1B).
Finally, we examined the impact of alemtuzumab levels on MC and secondary GF. Patients with day 0 alemtuzumab levels ≤0.32µg/mL had a lower CI of MC compared to patients with levels >0.32µg/mL, 14.3% vs 90.9%, respectively (p=0.03). The CI of secondary GF was 0% in patients with day 0 alemtuzumab levels ≤0.32µg/mL compared to 54.3% in patients with levels >0.32µg/mL (p=0.08).
Conclusions
This study demonstrates a strong relationship between alemtuzumab levels and durable engraftment. Further, interferon gamma activity, as reflected by CXCL9, inversely correlates with peri-transplant alemtuzumab levels in this prospective cohort treated with RIC. Our findings support the paradigm that higher alemtuzumab levels drive efficient T cell depletion of the stem cell product which increases the risk of MC and secondary GF, suggesting that donor T cells promote engraftment via a graft versus hematopoiesis function. Precision alemtuzumab dosing strategies may offer an opportunity to improve outcomes for patients who undergo RIC HCT.
Pulsipher: Adaptive: Research Funding; Equillium: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Jasper Therapeutics: Honoraria. Bollard: Neximmune: Current equity holder in publicly-traded company; Catamaran Bio: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Cabaletta Bio: Current equity holder in publicly-traded company, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Mana Therapeutics: Current equity holder in publicly-traded company, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Patents & Royalties; Cellectis: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Repertoire Immune Medicines: Current equity holder in publicly-traded company; ROCHE: Consultancy, Honoraria; SOBI: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Kean: Regeneron: Research Funding; Bristol Myers Squibb: Patents & Royalties: From clinical trial data, Research Funding; Bluebird Bio: Research Funding; Gilead: Research Funding; Vertex: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy; EMD Serono: Consultancy. Jordan: Sobi: Consultancy. Allen: Sobi: Consultancy.
Alemtuzumab, humanized monoclonal antibody against CD52, used as part of allogeneic HCT conditioning